Concurrency State Models Java Programs 2nd Edition
Concurrency: State Models & Java Programs. Second edition. The set of demonstration programs in the book. Concurrency: State Models and Java Programs. Second edition ** Revised by Daniel Sykes, 2013. State Models and Java Programs, 2nd Edition. Website also includes the full set of state models, java. Concurrency: State Models and Java Programs, 2nd.
. Aland Islands. Albania. Andorra.
Armenia. Austria. Azerbaijan. Belarus. Belgium. Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Bulgaria. Croatia.
Cyprus. Czech Republic. Denmark. Estonia. Finland. France.
Georgia. Germany. Gibraltar. Greece.
Greenland. Holy See (Vatican City State). Hungary. Iceland. Ireland.
Italy. Latvia. Liechtenstein. Lithuania. Luxembourg. Macedonia.
Malta. Moldova. Monaco. Montenegro. Netherlands.
Norway. Poland. Portugal.
Romania. Russia. Serbia. Slovakia. Slovenia. Spain.
Sweden. Switzerland. Turkey.
Ukraine. United Kingdom. American Samoa. Australia. Bangladesh. Bhutan. British Indian Ocean Territory.
Brunei. Cambodia. China.
Christmas Island. Cocos (Keeling) Islands. Cook Islands. Fiji. Guam. India. Indonesia.
Japan. Kazakhstan. Korea (the Republic of). Kyrgyzstan. Laos.
Malaysia. Maldives. Mongolia. Myanmar. Nepal. New Zealand.
Pakistan. Papua New Guinea. Philippines. Samoa.
Singapore. Solomon Islands. Sri Lanka. Tajikistan. Thailand. Timor-Leste.
Tonga. Turkmenistan. Uzbekistan. Vanuatu. Vietnam. Description Concurrency provides a thoroughly updated approach to the basic concepts and techniques behind concurrent programming.
Concurrent programming is complex and demands a much more formal approach than sequential programming. In order to develop a thorough understanding of the topic Magee and Kramer present concepts, techniques and problems through a variety of forms: informal descriptions, illustrative examples, abstract models and concrete Java examples. These combine to provide problem patterns and associated solution techniques which enable students to recognize the problems and arrive at solutions. 1.1 Concurrent Programs.
1.2 The Modeling Approach. 1.3 Practice. 1.4 Content Overview. Notes and Further Reading. Processes and Threads.
2.1 Modeling Processes. 2.2 Implementing Processes. Notes and Further Reading. Concurrent Execution.
3.1 Modeling Concurrency. 3.2 Multi-Threaded Programs. Notes and Further Reading. Shared Objects and Mutual Exclusion.
4.1 Interference. 4.2 Mutual Exclusion in Java. 4.3 Modeling Mutual Exclusion. Notes and Further Reading. Monitors and Condition Synchronization.
5.1 Condition Synchronization. 5.2 Semaphores.
5.3 Bounded Buffers. 5.4 Nested Monitors.
5.5 Monitor Invariants. Notes and Further Reading.
6.1 Deadlock Analysis. 6.2 Dining Philosophers Problem. Notes and Further Reading. Safety and Liveness Properties. 7.2 Single-Lane Bridge Problem. 7.3 Liveness. 7.4 Liveness of the Single-Lane Bridge.
7.5 Readers–Writers Problem. Notes and Further Reading.
Java Programs Pdf
Model-Based Design. 8.1 From Requirements to Models. 8.2 From Models to Implementation.
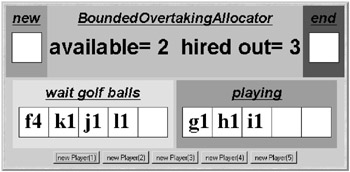
Notes and Further Reading Exercises. Dynamic Systems. 9.1 Golf Club Program. 9.2 Golf Club Model. 9.3 Fair Allocation.
9.4 Revised Golf Ball Allocator. 9.5 Bounded Overtaking. 9.6 Bounded Overtaking Golf Ball Allocator.
9.7 Master–Slave Program. 9.8 Master–Slave Model. Notes and Further Reading. Message Passing.
10.1 Synchronous Message Passing. 10.2 Asynchronous Message Passing. 10.3 Rendezvous.
Notes and Further Reading. Concurrent Architectures. 11.1 Filter Pipeline. 11.2 Supervisor–Worker. 11.3 Announcer–Listener. Notes and Further Reading. Timed Systems.
12.1 Modeling Timed Systems. 12.2 Implementing Timed Systems.
12.3 Parcel Router Problem. 12.4 Space Invaders.
Notes and Further Reading. 13.ihl Program Verification. 13.1 Sequential Processes. 13.2 Modeling Condition Synchronization. 13.3 Modeling Variables and Synchronized Methods.
13.4 Bounded Buffer Example. 13.5 Readers–Writers Example. Notes and Further Reading. Logical Properties. 14.1 Fluent Propositions. 14.2 Temporal Propositions.
14.3 Fluent Linear Temporal Logic (FLTL). 14.4 Database Ring Problem. Notes and Further Reading. Appendix A: FSP Quick Reference.
Appendix B: FSP Language Specification. Appendix C: FSP Semantics. Appendix D: UML Class Diagrams.